Plastic injection molding manufacturing
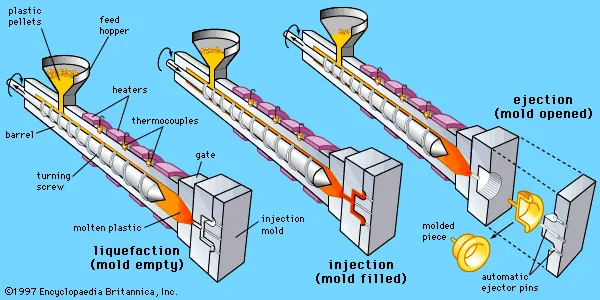
(Left) Plastic pellets are fed from a hopper into a reciprocating screw injection molding machine, where they are melted by the mechanical energy exerted by a turning screw and by heaters arranged along the barrel. (Centre) The screw moves forward, injecting the molten plastic into a mold. (Right) After the plastic has solidified, the mold is opened and the molded piece ejected.
A Quick intro to the injection molding process
Cost factors of an injection molding
Mold tool design; Mold tool manufacture; Polymer cost; Process cost
4 essential pieces of information! Your plastic injection mold needs to know
How big it is How many you need The plastic material it needs to be made of If the design is manufacturing-ready
The size of the molding effect:
Plastic material cost; Mold tool material; Mold tool machining time; Mold tool labor cost; Injection molding machine size
How many You cannot get 5,000 moldings for the same part price as 10,000 moldings
A smaller batch means a much higher cost per part; Check minimum orders; Multi-impression mold tools can mean huge savings per part
Which material? What does your plastic part really need to do?
UV resistant? Conductive? Functional at high or low temperatures? File retardant? A specific color or transparency?
Which material? Reasons to be careful with a material choice:
Higher material price; Longer cycle time; Higher mold tool cost; The danger of brand names
Is the design manufacturing-ready? That beautiful design can be impossible to make!
Plastic product design mold tool design; Anything can be made – at a price; An experienced molder will help you to avoid surprises
Melt processing of plastics and plastic injection molding
Plastic injection molding is a type of melt processing. ‘melt’ refers to the need to actually melt plastic granules (also known as resin) in an injection molding machine in order to produce the plastic product or component.
Plastic injection molding is a process that accounts for nearly half of the production of plastic.
This type of materials used in plastic injection molding is often abbreviated because of some of the long and sometimes complicated chemical names. These materials include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS injection molding), nylon (PA), poly carbonate (PC), polypropylene (PP) and polystyrene (GPPS). Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA injection molding )
Many different types of products are made using plastic injection molding ranging from precision components to consumer goods. We come into contact with many products produced by plastic injection molding on a daily basis.
Injection molded brand build phone headphone, the bumpers, dashboards and other bold plastic particle of our vehicles, the cardboards razors we cause to shave with, and direct our household wash basins and wheelie bins.
Plastic injection molding allows large amounts of identical items to be produces quickly and is much less lab our intensive than for example vacuum forming. This is because the plastic injection molding carries out the whole process of producing each plastic part of product.
How does plastic injection molding work?
The basic plastic injection molding process works as follows
The plastic injection molding machine has a heated barrel with a reciprocating screw inside.
Plastic sand is cram into the bitter pipe via a hopper on the cap of the machine.
The heating of the barrel and force and friction of the screw which is driven by a hydraulic motor melt the plastic into a molten liquid form.
The plastic is forced forward by the screw into the plastic injection molding tool.